
Should we use oil?
What are fossil Fuels?
The National Academies of Science defines Fossil Fuels as nonrenewable sources of energy formed millions of years ago, based on the remains of dead organisms. There are 3 different types of fossil fuels: coal, gas and oil which are all non-renewable and finite sources of energy. Fossil Fuels were formed over long period of time and we are using these resources much faster than they are produced. This means that one day, we will run out of fossil fuels as the stock will be used up.
Coal was made from dead plants materials while crude oil and gas were made of dead marine organisms. In order for fossil fuels to form, the organisms have to die in certain conditions which explain why some places are more keen to have fossil fuels than others as explained by EnergyQuest.ca.gov.
FOSSIL FUELS

Coal Surface Mining.

Crude Oil Rotary Drilling.

Natural Gas Fracking Well.
What are they used for?
USES
Fossil Fuels are widely used to produce energy and it is fair to say that our society greatly depends on them. According to National Academy of Science (NAS) 84% of the United State's energy come from Fossil Fuels. They can be in the form of coal, gas or oil and are used for various purposes such as electricity, transportation, heat, industry and manufacturing.
Coal is a cheap source of energy used to produce electricity. As stated on the NAS website, 50% of US's electricity comes from coal.
45% of oil used in the USA is used for transportation as reported by The Energy Information Administration and a large part is utilized in the industry such a to make plastics (click here for more information).
Natural gases make up 24% of US energy according to NAS. This type of fossil fuel, reputed to be a "cleaner" source of energy is used to produce electricity and heat and power industries.

I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. It's easy.
Where are fossil Fuels found?
SOURCE
According to the Environmental and Energy Study Institute, the location on fossil fuels depends on their origin: coal is made of plant material while crude oil and gas are made of dead marine organisms. In order to identify fossil fuels deposits, scientists use sound waves, as explained by the New Mexico Oil and Gas Association. Using geophones, they are able to determine the speed at which the waves travel. This velocity indicator reveals if the ground is made of solids, liquids or gases.
Coal, which is mainly made of plant material, can be found in almost every country in the world. The biggest producer of coal are USA, China, Russia and India.*
Crude oil comes from dead marine organisms. As well as coal, crude oil can be found all over the world but the Middle East itself represents 63% of the reserves.*
Natural Gas is also made of dead marine organisms. The largest known reserves in the world are located in the Middle East as well as Russia and USA.*

*Sources: American Petroleum Institute and University of Delaware.
How are fossil Fuels formed?
ORIGIN
Crude Oil and Natural Gases
According to BBC, Oil and Natural gases were formed millions of years ago out of microscopic marine plants and animals. When they died, these organisms sank to the bottom of the sea and released the carbon molecules absorbed in their bodies. Over time the layers of sediments accumulated and the amassment of deposits increased the temperature and pressure on the seabed. These organisms along with the surrounding biomass then turned into either oil or natural gas depending on the conditions.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration also mentions that the oil and natural gases later on usually migrate into the tiny pores in the ground rocks or are trapped between impermeable layers of deposits.
Coal
Coal was formed millions of years ago out of dead plants and trees. As these died, they fell into the swamp waters while more grew. Over time, this lead to an accumulation of rotting dead plants and sediment layers over Earth's surface. The mass of the amassment, heat, pressure and lack of oxygen caused the dirt and deposits to fuse and turn into coal as explained by the World Coal Association.

Formation Process of Crude Oil from Marine dead organisms.
ABOUT ME
EXTRACTION
According to the World Coal Association and the Kentucky University Geological Survey, coal is a solid fossil fuel which is dug out of the ground by mining. As shown by this diagram, there are two categories of mines: underground and surface mining methods. Underground mines include shaft, slope and drift mining. Open cast mines are based on methods which remove all rocks and sediments covering the coal, it can for example involve digging a pit or the mountain top.
How are fossil Fuels extracted?
Coal

Diagram of coal mining methods, including underground and surface mining techniques.
Crude Oil
In order to extract crude oil trapped in porous rocks, drilling methods are used. The first drilling method called percussion drill was created in 1859 by Edwin Drake. According to the American Oil and Gas Historical Society, this method consisted in a heavy bit attached to a four leg structure and a cable and pulley system. The rocks of the ground were broken down by dropping the drill bit over and over to extract the crude oil.
In the 1900s the rotary drilling process was invented, as explained by the New Mexico Oil and Gas Association. This method involves a derrick- the structure-, a bit attached to a pipe or drillstring as well as power systems. In order to dig down and reach the crude oil, the drillstring is twisted and the tip rotates causing the rock to break down. In order to take out the bits or rock, drilling mud-a chemical mixture-is constantly circulating through the pipe and out of the bit.
According to AdventuresInEnergy.org, there are three ways of pumping crude oil: primary, secondary and enhanced recovery.
Primary recovery mostly relies on undergrounds pressures to bring up crude oil. In addition to that, pumps are used to create a suction and draw the fluids up. In some cases, natural gases extracted are injected underneath the oil through the well. This method, mostly used offshore usually only extracts 10% of the oil deposit.
Secondary recovery is the most used technique to extract oil as mentioned by AdventuresInEnergy.org. This process involves the initial drilling phase and the recuperation of the extracted water. This wastewater is then separated from oil and re-injected into the ground in order to bring more oil to the surface. This method has several benefits: it increase the amount of oil extracted by 20% and disposes the wastewater back where is came from, therefore limiting the impact on the surrounding environment.
In order to exploit 60 additional percents of the remaining oil, enhanced recovery techniques are put to use. As precised by AdventuresInEnergy.org, this includes 3 main methods: thermal recovery, gas injection and chemical flooding. Thermal recovery aims at making the oil flow more easily and increase the underground pressure by injecting steam into the oil reserve. Gas injection follows the same method but the steam is here replaced with miscible or immiscible gases. Miscible gases include CO2, propane, methane or other gases which disolve in the oil and lower its viscovity while immiscible gases do not mix with the oil and aim at increasing the pressure in the reserve to bring more fluid to the surface.
As mentioned by the Global Marine Oil Pollution Information Gateway, recently these methods are also used off-shore in order to extract the crude oil under the sea. The platform can either have legs attached to the ocean floor, float with air-filled legs or be set up on a drillship.
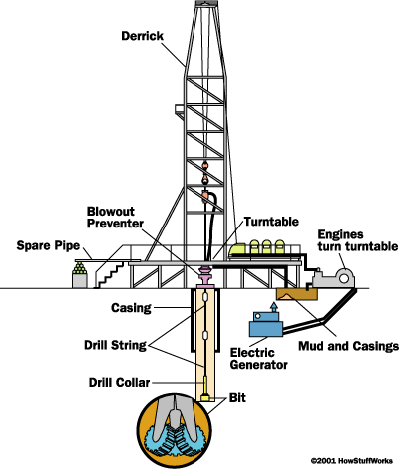
Diagram of a rotary drilling well.

Primary Recovery Diagram.

Secondary Recovery Diagram.

Enhanced
Recovery Diagram.

Picture of an off-shore oil well.
Natural Gas
According to national geographic, natural gas is mostly found near crude oil and sometimes extracted simultaneously with petroleum. Natural gases are mostly extracted through vertical drilling but there are several alternatives. Vertical drilling has limited access to resources as the well is restricted to the reserves it encounters. Therefore, in order to extract more natural gas from the shale and increase productivity, techniques such as hydraulic fracturing, horizontal drilling and acidizing have been created.
Hydraulic Fracturing, also known as the process of fracking, involves drilling vertically into the ground. Then streams of high-pressure water, chemicals and sand are injected in the porous rocks in order to break them up. This releases the natural gas which is then pumped up and transported in pipes as explained by what-is-fracking.com.
Horizontally drilling is another method which helps increase the productivity of a well. This process simply implies that the well is drilled vertically and then sideways- horizontally.
National Geographic defines acidizing as a method similar to fracturing. This process involves injecting hydrochloric acid in order to dissolve the rocks which stop the gas flow.

Diagram of a hydraulic fracturing natural gas well. This diagram also highlights its effects on the environment.
CONSEQUENCES
What are the consequences of the extraction and use of Fossil Fuels?
According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, the extraction and use of fossil fuel has several consequences on the environment, both local and global. These includes global warming, damage to land, acid rain and water and air pollution also linked to health problems.
The combustion of fossil fuels such as coal and oil released large amounts of carbon dioxide in the air. The Union of Concerned Scientists mentions that over the last 150 years, burning fossil fuels has resulted in more than a 25 percent increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere.
These gases contribute to the human enhanced greenhouse effect and trap solar radiations in our atmosphere. This causes global warming leading glaciers to melt and other natural catastrophes. Indeed, according to BBC, scientists have estimated that sea levels could rise between 10 and 90 cm over the next hundred years, therefore reducing habitable areas around the world. BBC also mentions that global warming linked with rising CO2 amounts in the atmosphere can affect weather patterns leading to flooding, hurricanes or droughts.
Furthermore, the exploitation of fossil fuels greatly contribute to general air, land and water pollution as mentioned by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. Accordingly, the Union of Concerned Scientists cites carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides and hydrocarbons as important pollutants produced by fossil fuel combustion.
The nitrogen oxides produced by fossil fuel combustion is defined as one of the main causes of smog and acid rains. Smog, which appear as clouds over many city skylines, causes lung irritations, bronchitis, pneumonias and respiratory infections. This phenomena, also known as tropospheric ozone, is a consequence of the reaction of non methane hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides to heat and sunlight as explained by the Union of Concerned Scientists.
Acid rains are mostly caused by excesses of nitrogen oxide and sulfur in the atmosphere, these gases are both produced in large quantities during the combustion of fossil fuels. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, acid rains forms when both of these toxic gases combine with water vapor and turn into sulfuric and nitric acids. These acids then fuse with the water contained in the clouds and fall on earth as rain or snow. These precipitations affect animals, buildings, plants and crops.
Moreover, the exploitation of fossil fuels exposes the local environment such as soil and water contamination caused by oil spills and drilling methods as mentioned by the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Oil spills are accidental water or soil contamination through pipelines, ships, trains or trucks which are used to convey oil from wells to refineries. According to Pacific Environment.org, oil exploitation and transportation poses great threats to fragile ecosystems, sometimes leading to devastating explosions, fires and degradations. The organizations also holds oil spills responsible for coast soiling, and the countless deaths of birds, marine fishes and other wildlife.
In addition to oil spills, fossil fuel extraction has other negative impacts on its environment such as reduction of water resources through pollution and drainage according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. This sources mentions that the fracking process used in order to extract natural gas requires large amount of water which is then mixed with chemicals and injected into the ground. In some areas, the significant drainage of water for natural gas extraction can affect the availability of water and impact aquatic habitats and animals. Besides, PriceOfOil.org makes reference to a study which has shown that between 20 to 85% of fracking fluids stay underground. As explained by National Geographic, the wastewater left behind after the fracking process is highly toxic and frequently radioactive and can leak and contaminate underground water sources. As well, the U.S. Energy Information Administration highlights the risk of earthquakes linked to the injection of non-treated wastewater into the ground.

Diagram of the Greenshouse effect and its consequences on Earth.

Picture of the melting ice cap as a consequence of the greenhouse effect.

Picture of smog over the city of Beijing linked to coal-burning industries.

Picture of the consequences of acid rain of vegetation and plants.

Picture of the Mexico oil spill which affected the ecosystem and industry of the area.

Diagram of the effect of hydraulic fracturing on water resources around wells.